What is Digital Printing?
Digital printing is the technique of printing visual or written content prepared in a computer environment onto different materials. Digital printing is performed on fabric using multi-pass machines in the weft direction and single-pass machines in the warp direction.
In conventional screen printing, color variety is limited. After selecting a few colors that are most present in the image, the final image is created by layering these colors on top of each other. For example, various shades of yellow are assigned to a single yellow color, and we see all of them as the same yellow color.
Digital printing, on the other hand, is created in a computer environment. It is the transfer of the work created in the computer to the fabric one-to-one. Whether the work is monochrome or multi-colored, it is possible to maintain the same color variety and liveliness without any tone loss. In digital printing, the increase in resolution is also one of the factors that increase the visual quality. Even the smallest details can be taken into account, and extremely realistic results can be obtained.
DPI (dots per inch) is a term used in digital imaging systems, which stands for “DOTS PER INCH,” meaning the number of dots per inch. As the resolution increases, the image quality increases proportionally.
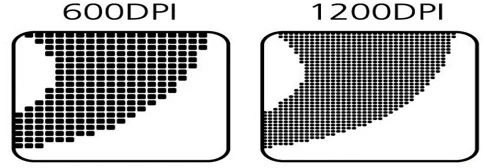
Resolution; it can be expressed as the number of pixels inside a screen that creates an image. In other words, the number of pixels on the screen, both vertically and horizontally, is called resolution. For example, if we assume a monitor with a resolution of 600×1200, its pixel count is calculated as 720,000.
Nozzle: A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow when it exits from a closed chamber or pipe. A nozzle is typically a tube or pipe with a varying cross-sectional area and can be used to direct or alter the flow of a fluid.
RIP: RIP program is a color and print management program developed for inkjet printers and textile printing. It creates ICC profiles that contain the necessary color adjustments to obtain the correct colors by comparing the scanned color with the original color. “Incoterms-2010”, which is regulated by the International Chamber of Commerce based in Paris, has introduced some rules to regulate international commercial disputes, conflicts, and legal disputes and to prevent loss of money and time for buyers and sellers.
What is Calibration?
It is the measurement of the color efficiency of the dye in the fabric in order to obtain the correct colors from digital printing machines.
Calibrations should be performed separately for dpi and fabric qualities.
It is done in 4 stages.
1- Limit check
2- Cutting excess dye
3- Linearity adjustment
4- Profile creation setting
DIGITAL PRINTING (PREPARATORY PATCHES)
Preparatory Patch for Dispersion Dyes
| Fiber | Application Process | |
| DIGIPRINT NP | PES | Scarfing |
Preparatory Pads For Acid Dyes
| Fiber | Application Process | |
| DIGIPRINT NP | PES | Scarfing |
Preparatory Pads for Reactive Dyes
| Fibers | Application Process | |
| DIGIPRINT R | CO,CV,LN | Coating, Sizing |



